The starting point is a band of material (usually foil or paper). A label is then applied to this material and repeated over the entire length of the material in regular intervals.
Parts (products), each with the same length, should be separated from this material in such a manner that the labeling on each individual product is located in the same position.
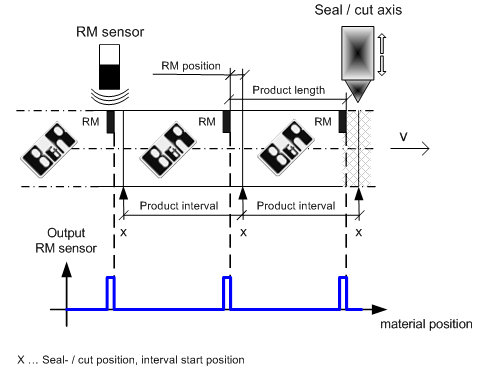
The material is transported to a seal/cut axis by a transport axis. This seal/cut axis cuts/seals the material for one product at a time. The material is then moved forward by one product length (product interval), the material for the next product is cut/sealed, etc.
Registration marks are put on the material in intervals of one product length at a time to accurately determine the position of the next cut.
If the material is now moved forward by exactly one product length (without taking tolerances such as during winding into account) and then a product is separated one after another, then the interval starting position from product to product shifts only minimally; this makes any "drifting" of the print on the individual products evident.
This shifting of the interval starting position depends on the machine speed as well as the type and quality of the material.
The shifting of the interval starting position can be corrected with registration mark control so that the individual products are always separated at the right position and labeling is located at the same position on the individual products.
The product length (equal to the distance between two registration marks) and the registration mark position (position of the registration mark within a product interval in reference to the interval starting position) are predefined.
A corresponding detection/control/compensation algorithm (registration mark control) applies a shift in the right direction, for example on the transport axis, in order to guarantee a properly made product in each cycle.
Registration mark control generally occurs in three steps:
•Checking the registration mark position, calculating and outputting the position error (MC_BR_RegMarkCalc001)
•Calculating the necessary shifting distance on the transport axis based on the position error (e.g. MC_BR_RegMarkCalc001 function block)
•Applying the shifting distance to the transport axis (e.g. with function blocks such as MC_Phasing, MC_BR_Phasing, MC_BR_Offset, or other individually programmed position and length corrections)